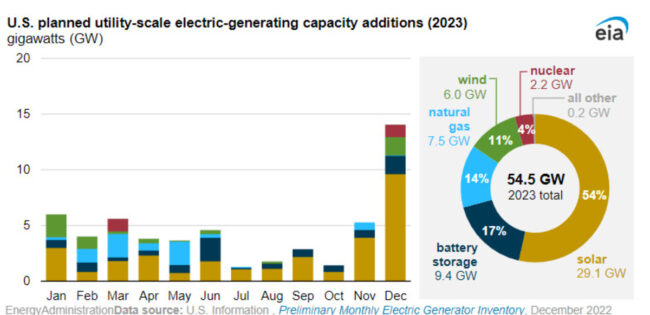
The Energy Information Administration (EIA) reported that U.S. developers intend to install 54.5 gigawatts (GW) of new electric generating capacity in 2023, with more than half being powered by solar energy.
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, under the Biden administration, includes around $370 billion for climate change and sustainable energy measures, including subsidies for solar and wind power.
This year is a big solar energy comeback
According to the EIA, solar power additions decreased by 23% in 2022 compared to 2021 due to supply chain problems and other issues brought on by the COVID-19 epidemic.
EIA anticipates that some of those 2022 projects that were postponed will start up in 2023 when developers intend to deploy 29.1 GW of solar power in the US, the report stated. That would equal around 53% of the new capacity that is anticipated.
Texas and California will take the lead in solar energy
With 7.7 GW and 4.2 GW, respectively, Texas and California will have the highest new solar capacity this year. These two states will provide 41% of the anticipated growth.
The amount of new utility-scale solar capacity installed in 2023 will surpass the previous record of 13.4 GW set in 2021 if all projects proceed as scheduled, according to the EIA.
According to the EIA, developers also intend to add 6.0 GW of wind capacity and 9.4 GW of battery storage to the 8.8 GW of battery storage currently available in the United States by 2023.
What are solar energy capacities in the U.S.?
The total installed solar energy capacity in the United States was over 110 gigawatts (GW). The U.S. continues to increase its use of solar energy and is among the leading countries in terms of installed solar capacity. Declining technology costs and pro-solar government policies have combined to fuel the rise of the solar industry in the United States.
The top states in the U.S. for installed solar energy capacity are:
- California
- Arizona
- North Carolina
- Nevada
- Texas
These states have a combination of favorable solar conditions, such as high levels of sunlight, and supportive policies. Such policies have encouraged the growth of the solar industry. California, in particular, has been a leader in the adoption of solar energy. In part, it’s due to its aggressive renewable energy goals and its supportive regulatory environment.
Energy Information Administration (EIA) data is reliable and impartial
Within the U.S. Department of Energy, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a statistical organization. In order to assist sensible policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of the role that energy plays in the economy and environment, the EIA’s primary duty is to collect, analyze, and disseminate information on the energy sector.
The EIA provides impartial, comprehensive data and analysis on a wide range of energy topics. It includes production, consumption, prices, imports, exports, reserves, and energy efficiency. The agency produces a variety of reports. Among them are the Annual Energy Outlook, the Monthly Energy Review, and the Short-Term Energy Outlook. They publish detailed data on specific energy sources. It encompasses petroleum, natural gas, coal, renewable energy, and nuclear power.
Policymakers, industry, and the media widely used the EIA’s data and analysis. And the public too. The aim is for them to make informed decisions about energy policy, investment, and operations.

